The Role of Local Government
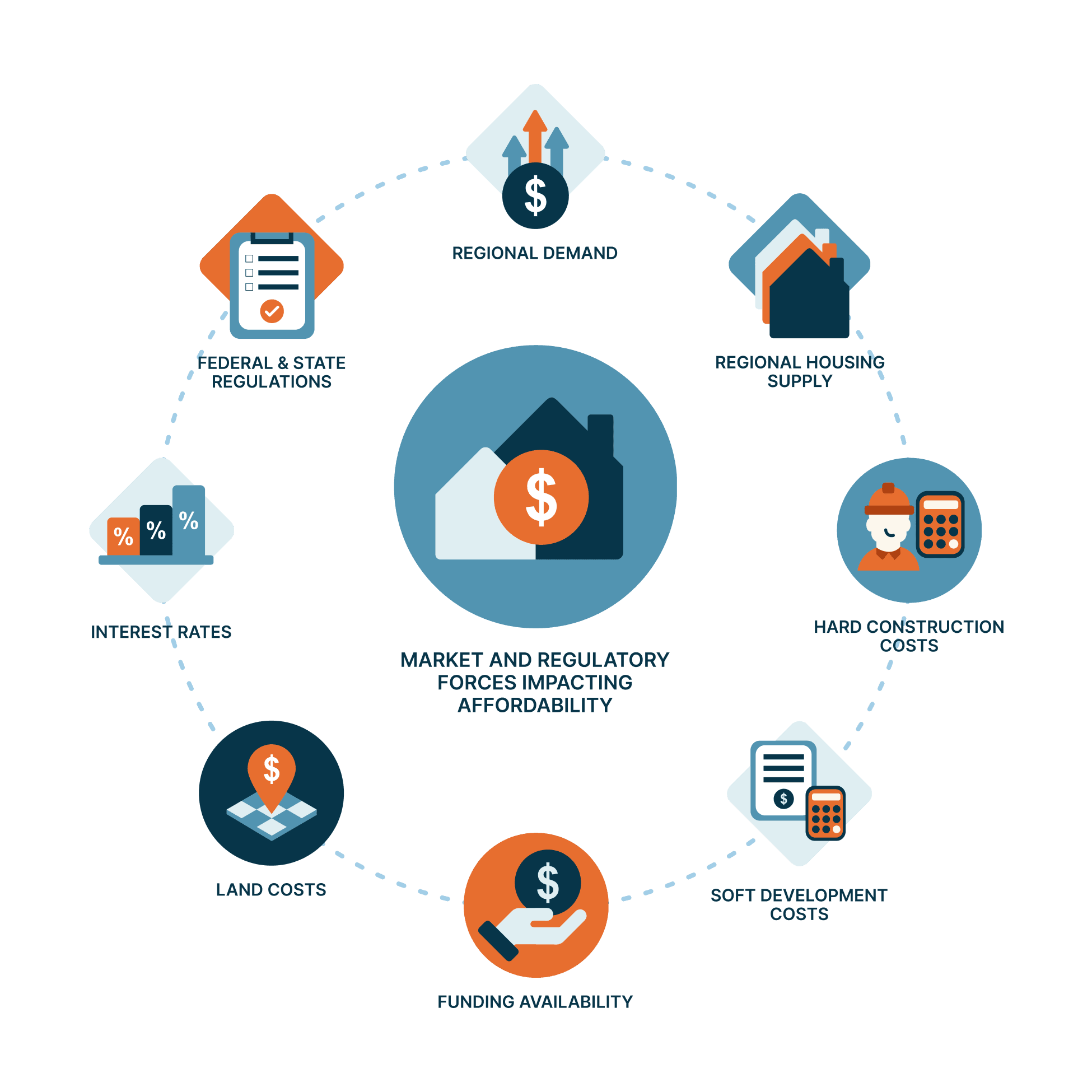
There are many factors that impact housing affordability at the local level, from macroeconomic trends affecting wages, interest rates and construction costs to regional job growth and housing supply to local land use policies that affect what can be built and the cost to build it. Local governments have a limited, but important set of tools to help create a healthy housing market.
Housing Policies and Programs Overview
Local governments primarily impact housing markets by setting the regulatory environment (land use) in which developers make investment decisions, by deploying public funds (subsidy) for infrastructure, amenities and development and by setting local policies (tenants’ rights) to balance the interests of tenants and property owners.
A healthy housing market requires policy makers to adopt a comprehensive approach that incorporates land use, subsidy and tenants’ rights. Each of these tools can help address different aspects of failures in a local housing market and are more effective and less costly when used together. However, very few communities in America have been able to adopt and implement a comprehensive approach to housing due to local political constraints.